LONDON: It was a moment that almost no one in the international community saw coming. On Saturday, during a routine meeting of the board of governors of the International Atomic Energy Agency in Vienna, Qatar’s ambassador to Austria delivered a surprise statement that added a dramatic new dimension to the ongoing Gaza peace talks in Doha.
The State of Qatar, Jassim Yacoub Al-Hammadi announced, was calling for “intensified international efforts” to bring all Israeli nuclear facilities “under the safeguards of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) and for Israel to join the Treaty on the Non-proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) as a non-nuclear state.”
The move, in the words of the director of the globally respected and independent Stockholm International Peace Institute (SIPRI), which has kept tabs on the world’s nuclear weapons and the states that possess them since 1966, “came out of a clear blue sky.”
There was no immediate response from Israel. But it seems certain that the Israeli delegation that was en route to Doha on Monday for a fresh round of talks, was taken surprise by a diplomatic ambush seemingly designed to introduce another bargaining chip into the negotiations.
Israel has never formally admitted possessing nuclear weapons, but its nuclear capability has been an open secret for decades.

According to SIPRI’s latest assessment, published last year in its 2024 Yearbook, by the start of last year nine states possessed approximately 12,121 nuclear weapons, of which more than 9,500 were considered available for immediate use — and Israel was most definitely one of those nine states.
Israel’s estimated stockpile of 90 warheads is not large, certainly not when compared with Russia’s 4,380 and America’s 3,708. If SIPRI’s carefully researched assessment is correct, only North Korea, with 50 warheads, has fewer nuclear weapons than Israel.
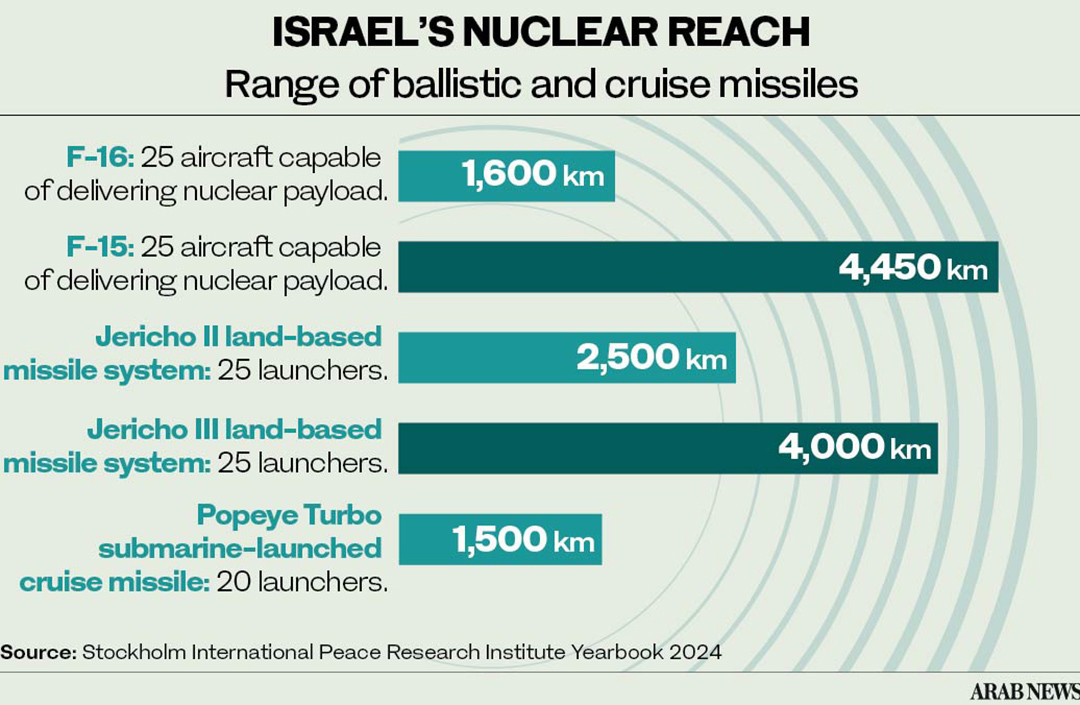
SIPRI’s assessment is that Israel has about 90 warheads, capable of being delivered anywhere within a maximum radius of 4,500 km by its F-15 and F-16I aircraft, its 50 land-based Jericho II and III missiles, and by about 20 Popeye Turbo cruise missiles launched from submarines.
But the size of Israel’s stockpile is irrelevant when set against the damage it could do, especially when its only likely target is Iran, which currently lacks the ability to retaliate — or to strike first — with nuclear weapons.
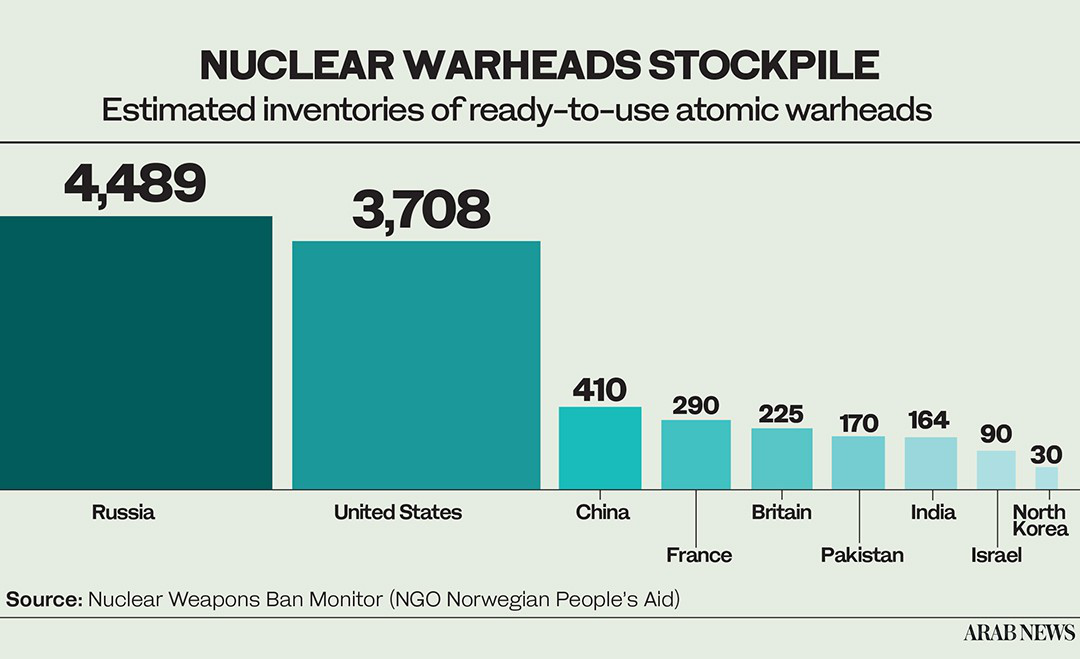
SIPRI concedes that, when it comes to Israel’s stockpile, “all figures are approximate and some are based on assessments by the authors.” Israel, it adds, “continues to maintain its longstanding policy of nuclear ambiguity, leaving significant uncertainty about the number and characteristics of its nuclear weapons.”
That ambiguity extends to Israel’s only official stated position on nuclear weapons, which it has repeated since the 1960s, that it “won’t be the first to introduce nuclear weapons into the Middle East.”
That, says SIPRI, is simply dissembling. Israeli policymakers, it says, “have previously interpreted ‘introduce nuclear weapons’ as publicly declaring, testing or actually using the nuclear capability, which Israel says it has not yet done.”
That, of course, raises the question of whether Israel’s nuclear weapons are home-grown or not. If not, the obvious supplier would be America.
But in 1979 reports emerged that a US satellite had detected the telltale double flash of a nuclear detonation over the Indian Ocean, roughly midway between Africa and Antarctica, raising the possibility that Israel had collaborated in a nuclear test with the apartheid-era South African government.
“Israel's nuclear capacity has always been a really quite strange phenomenon of Middle Eastern geopolitics,” said Dan Smith, Director of SIPRI.
“All five of the permanent members of the UN Security Council, each of which has nuclear weapons, are referred to in the Non Proliferation Treaty (NPT) as the nuclear weapon states and so are bound by the Treaty.
“Outside of the treaty, Israel, Pakistan and India never signed up for it, and North Korea did sign up for it, but then withdrew before developing its nuclear weapons.
“So, the three states that are nuclear armed, but not part of the NPT, all make explicit that they have nuclear weapons, and of course this is the point of a deterrent.
“The idea is, ‘You may not know exactly what hell I will rain down upon you, but you know I will rain down hell.’
“But Israel has come up with something different. It’s clear that they do have nuclear weapons, but they have never formally acknowledged it and in Israel it is not talked about.”
Israel has always taken extreme steps to protect its nuclear secrets.
“Israelis are scared,” said Ahron Bregman, a senior teaching fellow in the Department of War Studies at King’s College London’s Institute of Middle East Studies, who served in the Israeli army for six years in the 1980s.
“Even if you believe it is a good idea to restrict Israel’s behavior and make sure it doesn’t do anything stupid, you are scared to act because you know they will abduct you and put you in jail. Israel is very tough on those who reveal its secrets.”
This was precisely the fate that befell Mordechai Vanunu, an Israeli nuclear technician and peace activist, in 1986.
After Vanunu revealed details of Israel’s nuclear weapons program to a British newspaper, he was ensnared in the UK by a female Mossad agent posing as an American tourist. She persuaded him to accompany her to Rome, where he was kidnapped by other Mossad agents and spirited back to Israel on board an Israeli navy ship.
Vanunu was charged with treason and sentenced to 18 years in prison, much of which he spent in solitary confinement. Released in April 2004, he remains under a series of strictly enforced restrictions, which prevent him from leaving Israel or even speaking to any foreigner.
“We all believe that Israel has a nuclear capability,” said Bregman. “The fact that it found it necessary to catch Vanunu and put him in jail, and continues to impose strict limitations on him, just proves that it has probably got it.”
In its annual report last June, SIPRI reported that Israel was upgrading its plutonium-production reactor at Dimona, and modernizing its nuclear arsenal.
Smith thinks that, in seeking to bring Israel’s nuclear capability into the open and have it subjected to international scrutiny, Qatar is pursuing an agenda backed by the wider region.
“Israel’s nuclear monopoly has always been a huge irritant in geopolitics in the region for every other power, and at the 2010 Non-Proliferation Review Conference (held at UN headquarters in New York) the state parties agreed on the notion of a Middle East nuclear-weapons-free zone.
“For the Arab states, that was a major issue. For the US and some of the Europeans it was just something to agree to in order to keep everybody happy. Nobody really seriously expected they were going to force Israel to give up the nuclear weapons that it hasn’t formally acknowledged.
“But Qatar, I think, is now expressing that urge to bring Israel into the framework of a non-nuclear Middle East.”
This is, he believes, likely to be a serious attempt to introduce the issue of Israel’s nuclear arsenal into the Gaza talks.
“I take Qatari foreign policy very seriously,” he said. “I don’t think that they are into gestures or grandstanding. They take seriously the idea which has been written into the Qatari constitution that they are a state with a mission to try to spread peace in their region and in the world.
“The shaky ceasefire in Gaza was a product of a huge amount of effort by Qatar, among others. It’s not the first time they have been able to play that kind of role, so they strongly see themselves in this kind of mediating, bridge-building role.
“I don’t know what their assessment is, how they calculate this as being a good time to launch this initiative. But I take it seriously because it’s them.”
Israel is believed to have twice come close to wielding, and perhaps actually using, its nuclear weaponry.
In 2017 a claim emerged that, on the eve of the Arab-Israeli war in 1967, Israel had been on the cusp of unleashing a “demonstration” nuclear blast designed to intimidate its enemies in the event that it appeared it might lose the war and be overrun.
The plan was revealed in interviews with retired general Itzhak Yaakov, conducted by Avner Cohen, an Israeli American historian and leading scholar of Israel’s nuclear history, and published only after Yaakov’s death.
It was not the last time Israel reportedly came close to bringing nuclear disaster to the region. In 2003 Cohen revealed that during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, when it appeared that Israeli forces were about to be overrun, then Prime Minister Golda Meir had authorized the use of nuclear bombs and missiles as a last-stand defense.
This doomsday plan, codenamed Samson, was named after the biblical strongman who, while captured by the Philistines, pulled down their temple’s pillars, killing himself and his enemies. And the shadow of an Israeli-triggered nuclear calamity continues to haunt the region.
In its 2024 report SIPRI noted that in the wake of the Hamas attack on Israel in October 2023 “several Israeli policymakers and commentators — including a minister who was later suspended from the cabinet — suggested that Israel should use nuclear weapons against Hamas fighters in Gaza.”
The International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons (ICAN), a coalition of non-governmental organisations in 100 countries that promotes implementation of the UN Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons, welcomed Qatar’s initiative.
“As Israel’s nuclear arsenal is an open secret, it is long past time that its nuclear facilities are subject to international safeguards,” said Susi Snyder, ICAN’s Program Coordinator.
“Joining the NPT should be a first step followed by Israel and other countries in the region joining the United Nations Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons and the proposed Middle East Zone Free of Nuclear Weapons and Other Weapons of Mass Destruction.
“Eliminating Israel’s nuclear weapons and ensuring that no other state in the Middle East ever acquires such weapons will be vital for the long-term security of all people in the region.
“Without disarmament, true peace will remain elusive.”




























